Which of the Following Can Be Determined by Amniocentesis and Karyotyping
Karyotyping can be done from blood, hair, or any other tissue. However, most karyotyping for medical diagnostic purposes is done on embryonic or fetal cells from unborn babies all the same in the uterus. The cells are usually collected by i of 2 methods: amniocentesis ![]() or chorionic villi sampling
or chorionic villi sampling ![]() . Preliminary testing is at present normally washed with a less invasive ultrasound examination of the fetus inside the uterus and an analysis of specific fetal chemicals in the female parent'southward blood. The goal of all of these tests is to determine whether or not the baby will be abnormal. This information can be the basis for a decision to perform an ballgame or to set up parents for the difficulties of raising a child with serious abnormalities and wellness problems.
. Preliminary testing is at present normally washed with a less invasive ultrasound examination of the fetus inside the uterus and an analysis of specific fetal chemicals in the female parent'southward blood. The goal of all of these tests is to determine whether or not the baby will be abnormal. This information can be the basis for a decision to perform an ballgame or to set up parents for the difficulties of raising a child with serious abnormalities and wellness problems.
Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis involves sampling the liquid immediately surrounding a fetus within the amnion ![]() (or amniotic sac) as illustrated below. This amniotic fluid is extracted through the mother's abdominal and uterine
(or amniotic sac) as illustrated below. This amniotic fluid is extracted through the mother's abdominal and uterine ![]() walls with a hypodermic needle. Local anesthesia is used for this test. The amniotic fluid by and large contains fetal urine but likewise has millions of fetal skin cells that tin can be cultured to produce a karyotype. Ultrasound monitoring is commonly used to avoid harming the fetus with the needle. This entire procedure only takes a few minutes in a doctor'south function.
walls with a hypodermic needle. Local anesthesia is used for this test. The amniotic fluid by and large contains fetal urine but likewise has millions of fetal skin cells that tin can be cultured to produce a karyotype. Ultrasound monitoring is commonly used to avoid harming the fetus with the needle. This entire procedure only takes a few minutes in a doctor'south function.
| | |
| Normal human fetus at |
Complete results of amniocentesis tests usually come back from the laboratory in 3-4 weeks. However, decision of gender often can be made in 1-2 days. At that place is 99+% accuracy in diagnosing Down syndrome ![]() and most other gross chromosomal aberrations including neural tube defects
and most other gross chromosomal aberrations including neural tube defects ![]() such as spina bifida
such as spina bifida ![]() . Amniocentesis tin be used to observe the presence of about 400 specific genetic abnormalities in a fetus. These now include some unmarried-gene mutations such as the one that is responsible for the blood disorder beta-thalassemia.
. Amniocentesis tin be used to observe the presence of about 400 specific genetic abnormalities in a fetus. These now include some unmarried-gene mutations such as the one that is responsible for the blood disorder beta-thalassemia.
Amniocentesis usually is washed from the 15th or 16th calendar week after conception on up to the 20th week. In other words, it is in the 2d trimester, which is relatively late. Only at this point in a pregnancy is at that place sufficient amniotic fluid to allow some of information technology (well-nigh 20 cc) to be fatigued off without significant danger to the fetus--there is only nearly .three- .five% take chances of the procedure causing a miscarriage. In some cases, amniocentesis is done as early on as the 12th-14th week, but the risk of miscarriage is twice every bit loftier and the accuracy in detecting neural tube defects is slightly lower.
A variation of the amniocentesis procedure described above involves testing a sample of claret extracted from the umbilical cord. This has an every bit loftier accuracy in diagnosing gross chromosomal abnormalities.
NOTE : Some medical facilities are now using an boosted method to examination amniotic fluid collected by amniocentesis. This new procedure is referred to as QF-PCR (quantitative fluorescent polymerase chain reaction). This allows for a more rapid discovery of abnormal chromosome numbers for chromosomes xiii, 18, 21, and 10. QF-PCR is still more often than not considered to exist experimental. Enquiry is besides ongoing to be able to use amniocentesis for the purpose of detecting a range of unmarried-gene mutations including those responsible for cystic fibrosis and Tay-Sachs disease.
Chorionic Villi Sampling (CVS)
With chorionic villi sampling (or biopsy), a small sample of chorion cells are collected for karyotyping. The chorion is a membrane that develops around an embryo ![]() and contributes to the formation of the placenta
and contributes to the formation of the placenta ![]() . Afterwards, every bit a fetus develops, the chorion fuses with the amnion. The biopsy
. Afterwards, every bit a fetus develops, the chorion fuses with the amnion. The biopsy ![]() usually is done past inserting a small flexible plastic tube through the vagina
usually is done past inserting a small flexible plastic tube through the vagina ![]() and the neck
and the neck ![]() into the uterus to draw out a sample of chorion tissue. Alternately, the cells may be extracted with a hypodermic needle through the abdominal and uterine walls, as in the amniocentesis procedure. Local anesthesia also is used for this test. Ultrasound monitoring helps to foreclose damage to the unborn child.
into the uterus to draw out a sample of chorion tissue. Alternately, the cells may be extracted with a hypodermic needle through the abdominal and uterine walls, as in the amniocentesis procedure. Local anesthesia also is used for this test. Ultrasound monitoring helps to foreclose damage to the unborn child.
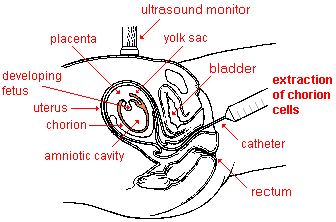 |
| Extraction of a sample of chorion cells |
Chorionic villi sampling usually is done starting time in the 10th-twelfth calendar week of pregnancy. That is still during the 1st trimester when the fetus is quite immature. Final laboratory results usually come dorsum in two weeks or less. However, the reliability of those results is less than with amniocentesis. In that location is approximately 98% accuracy in diagnosing Down syndrome and some other conditions associated with gross chromosomal abnormalities. Still, the accuracy in predicting neural tube defects is lower with CVS. The chance of miscarriage is at least i-3%, or 2-6 times higher than with amniocentesis. As a consequence, chorionic villi sampling is less oft performed. The risk can exist reduced past performing the biopsy no earlier than the 10th week of a pregnancy.
Screening with Maternal Blood
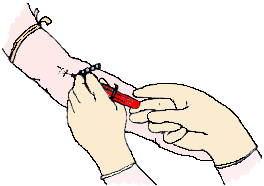 | |
| Blood being drawn from a significant woman for AFP and other fetal chemic screening |
A much more routinely done diagnostic procedure for pregnant women is testing their blood for alpha-feto poly peptide ![]() and several other chemicals originating from their fetus . This screening is significantly less expensive and has no hazard of causing a miscarriage. However, the information gained is less reliable in predicting a chromosomal abnormality. Therefore, positive AFP results are usually followed up by amniocentesis for verification.
and several other chemicals originating from their fetus . This screening is significantly less expensive and has no hazard of causing a miscarriage. However, the information gained is less reliable in predicting a chromosomal abnormality. Therefore, positive AFP results are usually followed up by amniocentesis for verification.
Alpha-feto protein is a substance normally produced by the liver of fetuses and is carried in their blood. Some of the fetal claret leaks into the placenta and then into the mother's blood during pregnancy. The AFP, and other diagnostic fetal and maternal chemicals, tin be separated from a blood sample taken from the mother'due south arm. Unusually high or depression amounts of AFP relative to the stage of pregnancy indicate that there may be particular kinds of genetic defects. Specifically, it may signal the likelihood of Down's syndrome, neural tube defects, abdominal wall defects, and trisomy 18 ![]() .
.
AFP testing is routinely done in the 14th to 20th week of a pregnancy. If the engagement of conception has been miscalculated, a false positive test result can occur. A similar error can happen if it is unknown that there are twins, because two fetuses produce more AFP than one.
Other substances of fetal origin establish in a female parent'southward claret that are commonly tested for in addition to AFP are the hormones HCG (human being chorionic gonadotropin) and unconjugated estriol. The combined testing procedure is referred to as Alpha-fetoprotein Plus or triple screening . Recently, testing for inhibin has besides been added to the combined screening. Subsequently, the examination is referred to as quadruple or quad screening . The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists guidelines now recommend that all meaning women have triple screening blood tests and ultrasound testing in the first trimester of their pregnancies.
Notation : Man chorionic gonadotropin is produced by the embryo and later in a pregnancy by the placenta. Unconjugated estriol is a course of estrogen that is fabricated by the liver of the fetus and past the placenta. Inhibin-A is a hormone that plays a office in regulating the menstrual bicycle. It is produced normally by the ovaries just also by the placenta during a pregnancy. A newer diagnostic blood exam used past some doctors looks for the presence of PAPPA (pregnancy-associated plasma protein A). Still some other new test (MaterniT21 LTD) that as well involves sampling maternal claret is likely to testify the nearly reliable for diagnosing Down syndrome. Different the other procedures, it does not look for fetal proteins merely rather for fetal DNA. Early on indications are that it may exist 99.1% accurate and have a low false positive charge per unit.
High-resolution Sonogram Screening
The about time to come of pregnancy screening for birth defects is likely to focus on the new generation of high-resolution ultrasound devices that are at present becoming available. They are first to exist used past doctors who have been peculiarly trained to discover the early on anatomical signs associated with some abnormalities. Using this procedure, Down syndrome tin be reliably detected in the first trimester of a pregnancy. In addition, it is possible to detect structural defects such as brain cysts and cleft-palates. An reward of high-resolution sonograms for screening is that they exercise non increment the risk of miscarriage and can be done early in a pregnancy. In addition, they are relatively inexpensive and quick since there are no samples to be processed in a laboratory. However, it is unlikely in the near future that amniocentesis will stop being considered the gilded standard for detecting chromosomal abnormalities.
Screening for Abnormal DNA and RNA Sequences
Somewhat further in the hereafter will be prenatal blood tests to find and analyze a broad range of abnormal fetal Dna and RNA sequences plant in a pregnant woman'south blood. Such tests would have the advantages of existence relatively inexpensive and noninvasive while providing highly authentic results. One such diagnostic procedure to notice Downward syndrome, chosen MaterniT21, has been developed and is being tested now. Early on results indicate that it may be 99.i% accurate with no risk for the fetus. This and other tests may largely replace amniocentesis in the future.
![]() Finding Disease Genes--from the PBS Nova series video Cracking the Code of Life
Finding Disease Genes--from the PBS Nova series video Cracking the Code of Life
This link takes you to an external website. To render here, you must click the
"dorsum" push button on your browser program. (length = 9 mins, 27 secs)
NOTE : additional tests for 24-29 mostly rare genetic and metabolic diseases are now routinely done with a little blood taken from the heel of newborn babies. These tests are mandated by law in all 50 U.S. states. One such test is for detecting phenylketonuria (PKU), an inherited disorder that causes mental retardation and other neurological problems.
Copyright � 1998-xx12 by Dennis O'Neil. All rights reserved.
illustration credits
Source: https://www2.palomar.edu/anthro/abnormal/abnormal_2.htm
.jpg)
0 Response to "Which of the Following Can Be Determined by Amniocentesis and Karyotyping"
Post a Comment